Reading:
If, for each (or at least sufficiently many) combination of covariates
in a data set, there are several observations, we can carry out an
extra sum of squares F-test to see if our regression model is adequate.
Suppose that
![]() are the distinct rows of the design matrix
and suppose we have n1 observations for which the covariate values are those
in x1, n2 observations with covariate pattern x2 and so on. Of course
are the distinct rows of the design matrix
and suppose we have n1 observations for which the covariate values are those
in x1, n2 observations with covariate pattern x2 and so on. Of course
![]() .
We compare our final fitted model with a so-called
saturated model by an extra sum of squares F-test. To be precise we
let
.
We compare our final fitted model with a so-called
saturated model by an extra sum of squares F-test. To be precise we
let ![]() be the mean value of Y when the covariate pattern is x1,
be the mean value of Y when the covariate pattern is x1,
![]() the mean corresponding to x2 and so on. Relabel the n data points
as
the mean corresponding to x2 and so on. Relabel the n data points
as
![]() and fit a one way ANOVA model
to the Yi,j. The error sum of squares for this FULL model is
and fit a one way ANOVA model
to the Yi,j. The error sum of squares for this FULL model is
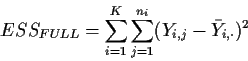
As an example return to the plaster hardness data of Lecture 12 There are 9 different covariate patterns corresponding to all the possible combinations of the 3 levels of SAND and 3 levels of FIBRE. There are two ways to compute the pure error sum of squares: create a new variable with 9 levels which labels the 9 categories or fit a two way ANOVA with interactions:
| 0 | 0 | 1 | 61 | 34 |
| 0 | 0 | 1 | 63 | 16 |
| 15 | 0 | 2 | 67 | 36 |
| 15 | 0 | 2 | 69 | 19 |
| 30 | 0 | 3 | 65 | 28 |
| 30 | 0 | 3 | 74 | 17 |
| 0 | 25 | 4 | 69 | 49 |
| 0 | 25 | 4 | 69 | 48 |
| 15 | 25 | 5 | 69 | 43 |
| 15 | 25 | 5 | 74 | 29 |
| 30 | 25 | 6 | 74 | 31 |
| 30 | 25 | 6 | 72 | 24 |
| 0 | 50 | 7 | 67 | 55 |
| 0 | 50 | 7 | 69 | 60 |
| 15 | 50 | 8 | 69 | 45 |
| 15 | 50 | 8 | 74 | 43 |
| 30 | 50 | 9 | 74 | 22 |
| 30 | 50 | 9 | 74 | 48 |
SAS CODE
options pagesize=60 linesize=80; data plaster; infile 'plaster1.dat'; input sand fibre combin hardness strength; proc glm data=plaster; model hardness = sand fibre; run; proc glm data=plaster; class sand fibre; model hardness = sand | fibre ; run; proc glm data=plaster; class combin; model hardness = combin; run;
EDITED OUTPUT (Complete output)
Sum of Mean
Source DF Squares Square F Value Pr > F
Model 2 167.41666667 83.70833333 11.53 0.0009
Error 15 108.86111111 7.25740741
Corrected Total 17 276.27777777
_______________________________________________________________
Sum of Mean
Source DF Squares Square F Value Pr > F
Model 8 202.77777778 25.34722222 3.10 0.0557
Error 9 73.50000000 8.16666667
Corrected Total 17 276.27777778
_______________________________________________________________
Sum of Mean
Source DF Squares Square F Value Pr > F
Model 8 202.77777778 25.34722222 3.10 0.0557
Error 9 73.50000000 8.16666667
Corrected Total 17 276.27777778
From the output we can put together a summary ANOVA table
| Source | df | SS | MS | F | P |
| Model | 2 | 167.417 | 83.708 | ||
| Lack of Fit | 6 | 35.361 | 5.894 | 0.722 | 0.64 |
| Pure Error | 9 | 73.500 | 8.167 | ||
| Total (Corrected) | 17 | 276.278 |